Accepted for publication in IEEE Transaction in Automation Science and Engineering (T-ASE), 2022
Description:
Machine learning and Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) can be powerful tools to model complex systems like robots.
In fileds like surgery, robots are very complex, and analytical models are hard to compute. Having an accurate model is, however, fundamental in order to ensure safety and precise motion, espeially becuase sensors can hardly be used in such scenarios.
One major limitiation of ANN, is that they are deterministic, meaning that they only provide a “punctual” prediction, given an input.
However, the models and the data have uncertainties themselves, and an estimation of these uncertainties could be beneficial to have an estimation of the confidence level of the model.
Probabilistic Neural Networks can solve this problem. Approaches like Bayesian Neural Networks (BNN) and Evidential Neural Networks (EvNN) allow having not only the model’s prediction, but also the setimation of the model’s uncertainty (epistemic undertainty) and data uncertainty (aleatoric uncertainty).
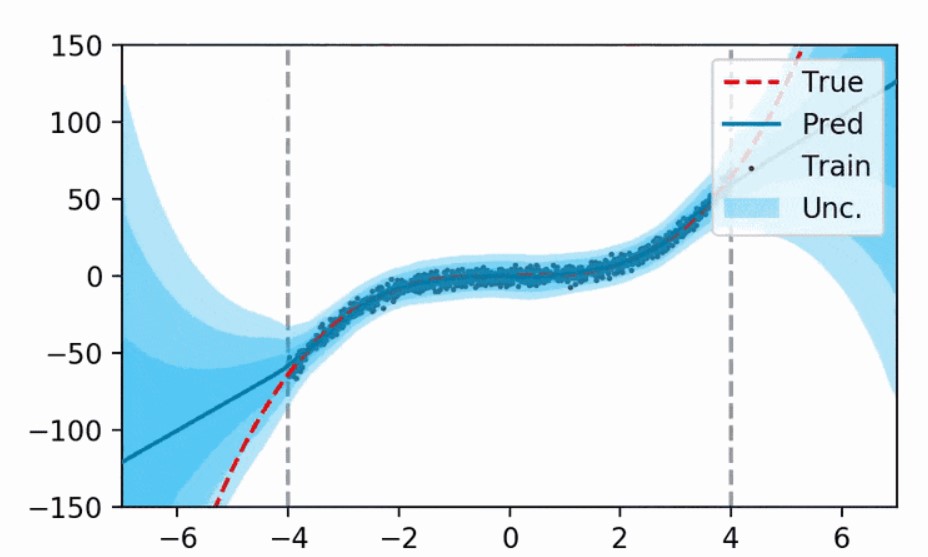
In this work we propose the use of BNN and EvNN to model the forward kinematics of a surgical robot.
The surgical instrument is mounted on top of a serial-link manipulator in a macro-micro manipulator setup.
For the control of the overall system, to perform a surgical task, we employ Hierarchical Quadratic Programming (HQP) in order to exploit the hyper-redundancy of the system and impose two prioritized tasks:
1) ensuring fulcrum effect at the insertion point location, also known as Remote Centr of Motion (RCM) constraint;
2) tracking a given path, to simulate a tumor resection task.
Additioanlly, we include a lower level task solved by means of a Sequential Qudaratic Programming (SQP) probelm in order to minimize the model’s uncertainty during operation and ensure the robot perfroms the task with the highest confidence possible.
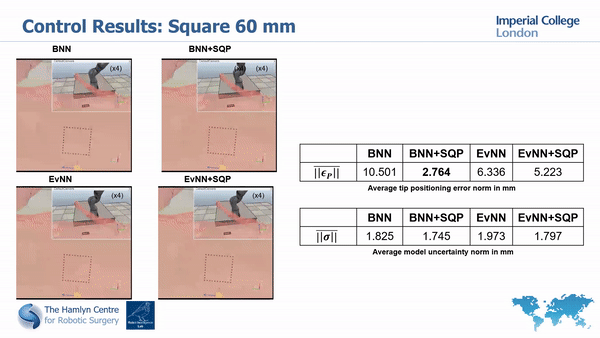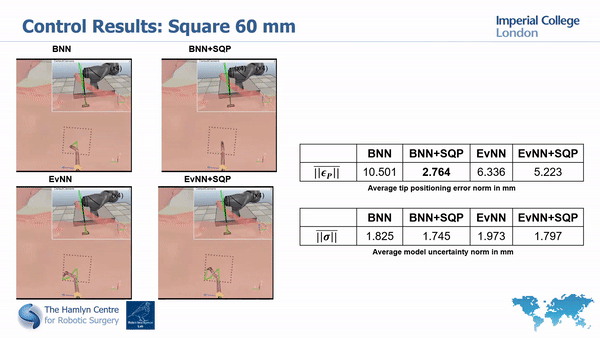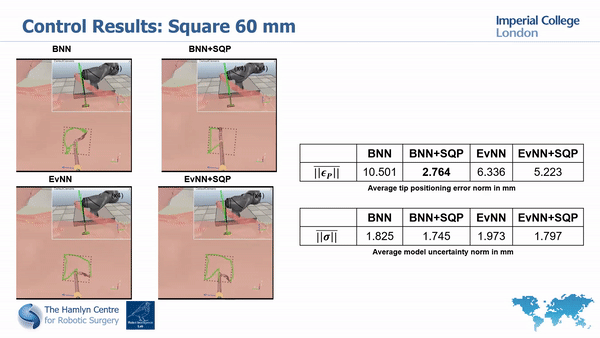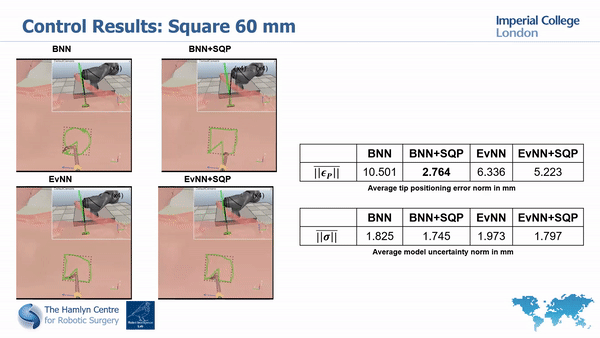

Our simulation and real world tests show the importance of minimizing model’s unceratinties in order to guarantee safety and improve task execution.
In fact, without the uncertainty minimization, the robot doesn’t manage to accurately track the desired paths; much higher accuracy is instead achieved with our proposed approach.